
Income tax is a crucial aspect of the financial landscape in India, affecting both individuals and businesses. It is a direct tax levied by the government on the income earned by individuals, companies, and other entities within its jurisdiction. Income tax returns, on the other hand, are the formal documents filed by taxpayers to report their income, deductions, and tax liabilities to the tax authorities.
Income Tax Returns (ITR) refers to the form that individuals, businesses, and other entities use to report their income earned during a financial year (April 1 to March 31) and the corresponding taxes paid on that income to the Income Tax Department of the Government of India.
Filing an income tax return is a legal obligation for individuals and entities meeting certain income thresholds or having specific financial transactions. The ITR form requires taxpayers to provide details about their income from various sources, deductions, exemptions, and taxes paid. The information provided in the ITR helps determine the taxpayer’s tax liability or refund.
The Income Tax Department provides different types of ITR forms based on the taxpayer’s income sources, such as ITR-1 (Sahaj), ITR-2, ITR-3, ITR-4, and so on. Each form caters to different categories of taxpayers, such as salaried individuals, self-employed individuals, businesses, and professionals. The government regularly updates the ITR forms, so it is important to use the correct form applicable to an individual’s situation while filing their ITR.
| Old Tax Regime | New Tax Regime | ||
| Income Tax Slab | Income Tax Rate | Income Tax Slab | Income Tax Rate |
| Upto INR 2,50,000 | NIL | Upto INR 2,50,000 | NIL |
| INR 2,50,001 – INR 5,00,000 | 5% | INR 2,50,001 – INR 5,00,000 | 5% |
| INR 5,00,001 – INR 10,00,000 | 20% | INR 5,00,001 – INR 7,50,000 | 10% |
| Above INR 10,00,000 | 30% | INR 7,50,001 – INR 10,00,000 | 15% |
| INR 10,00,001 – INR 12,50,000 | 20% | ||
| INR 12,50,001 – INR 15,00,000 | 25% | ||
| Above INR 15,00,000 | 30% | ||
ITR filing is the process of submitting an individual’s annual income tax return to the Income Tax Department of India. It is a legal requirement for all citizens and residents of India who earn a taxable income. Filing an ITR is an important and extensive process as it requires clear knowledge of the tax brackets and various rules. ITR filing refers to the documentation of an individual’s or their business’s income tax paid in that particular financial year. Varying on the category or the type of business one is involved in, salaried or self-employed, there are various forms one has to file accordingly.
All companies must file their IT returns, irrespective of whether or not they had business operations within that fiscal year. Companies must file income tax returns whether they make a profit or a loss. Prior to the deadline for filing returns, partnership firms must submit a NIL income tax return. The requirement to file returns applies even to defunct businesses that haven’t made any business decisions in a year.

When it comes to choosing the right ITR form for small businesses, there are several factors to consider. The selection depends on the nature and type of business, the income generated, and other relevant criteria. Here are some guidelines to help a small business owner to choose the appropriate ITR form:
Determine the legal structure of the small business. Common structures include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability partnership (LLP), and company. The ITR forms differ based on the type of business entity.
Get familiar with the various ITR forms available. The Income Tax Department has a list of ITR forms specific to different types of taxpayers. Each form is designed to capture specific information related to income, deductions, and exemptions. Here are the various types of ITR forms available in India:
| ITR FORM | Eligibility |
| ITR – 3 | To be filed by a person who earns a living via a business or occupation. |
| ITR – 4 (SUGAM) | Businesses other than LLPs that are subject to presumptive tax schemes and have annual gross revenues up to Rs. 50 lakhs are required to file this. Sections 44AD, 44ADA, and 44AE govern the calculation of their income. |
| ITR – 5 | For LLPs and partnerships that do not file an ITR 7. |
| ITR – 6 | For those businesses who do not assert exemption under Section 11. |
| ITR – 7 | Solely for businesses that must file returns under Sections 139(4A), 139(4B), 139(4C), and 139(4D). |
Evaluate the sources of income generated by the small business. For example, if one receives income from salary, house property, and small business, they need to choose a form that accommodates all these sources.
If a person is eligible for presumptive taxation under the tax laws, their turnover may be a determining factor in selecting the appropriate ITR form. Certain forms are specifically designed for small businesses with a turnover below a specified threshold.
If a small business is subject to a mandatory tax audit as per the tax laws, the owner needs to choose the corresponding ITR form. The tax audit threshold may vary depending on the type of small business entity and turnover.
A person should ensure that they meet the eligibility criteria specified for each ITR form. Some forms may have specific conditions related to income, profession, or residency status.
To file ITR, an individual will typically need the following documents and information:
Businesses can avail various exemptions and deductions to reduce their tax liability. These exemptions are provided under the Income Tax Act 1961 and are subject to specific conditions and limits. Here are some common exemptions available to businesses:
Businesses can claim deductions for various expenses incurred in the course of their operations, such as employee salaries, rent, utilities, travel expenses, advertising costs, etc. These deductions help in reducing the taxable income of the business.
Businesses can claim depreciation on assets used in their operations, such as machinery, equipment, buildings, etc. Depreciation allows for the gradual reduction in the value of these assets over time and provides a deduction from taxable income.
Companies engaged in scientific research and development activities can avail of tax deductions for R&D expenses incurred. This deduction encourages innovation and technological advancement in businesses.
Startups registered under the Startup India initiative may enjoy tax benefits and exemptions for a specified period. These include a three-year tax holiday in the first seven years of existence, exemption from capital gains tax on the sale of specified assets, and tax benefits for investments made by eligible investors.
The government provides sector-specific incentives to promote certain industries. For example, deductions or exemptions may be available for businesses engaged in infrastructure development, renewable energy, agriculture, healthcare, etc.
Apart from these, there are several other exemptions which are applicable to all the taxpayers:
Receipts and documents related to investments made under various tax-saving schemes like Provident Fund (PF), Public Provident Fund (PPF), National Savings Certificates (NSC), etc.
Premium payment receipts for health insurance policies eligible for tax deductions.
Receipts or certificates for donations made to eligible charitable institutions.
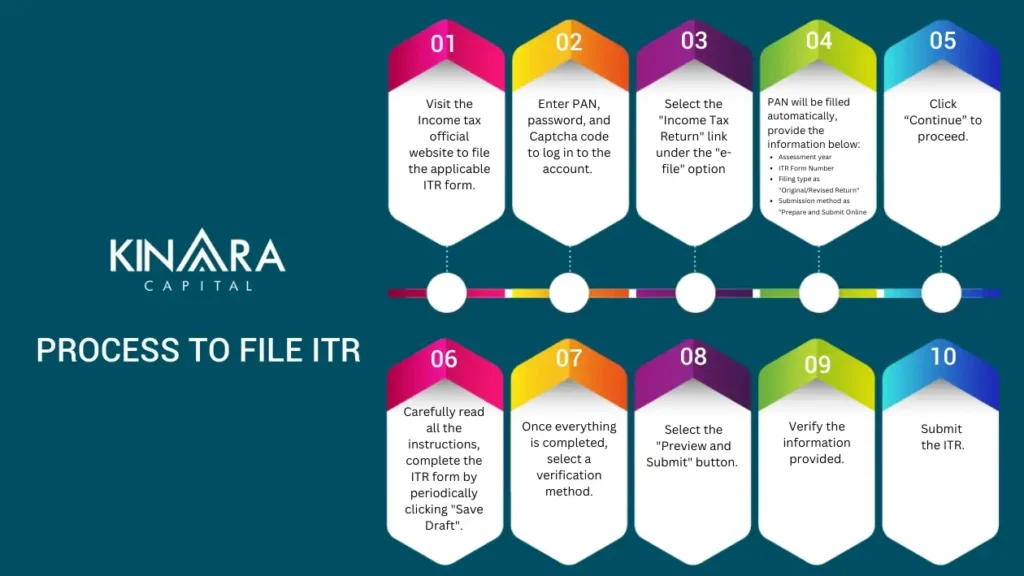
Companies and self-employed people can submit income taxes in two different ways for their operations. The first approach is an online one, whereas the second is an offline one. Filing ITR is typically done online through the Income Tax Department’s official website or authorized e-filing portals, here’s the process:
The implications of late filing of ITR can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the regulations of the country in question. However, here are some general implications of late ITR filing:
If a person is entitled to a tax refund, filing their ITR late may result in a delay in receiving the refund. This means they lose out on any interest that could have accrued on that refund amount.
Filing ITR late may restrict a person’s ability to revise their tax returns in case they make any errors or omissions. In some jurisdictions, there may be a time limit within which revisions can be made, and late filers might miss this opportunity.
Late filers may attract additional scrutiny from tax authorities, increasing the chances of being selected for a tax audit or investigation. This can be time-consuming and stressful, requiring to provide additional documentation and explanations to the tax authorities.
In certain situations, late ITR filing can affect an individual’s ability to obtain loans or financial services. Financial institutions often require tax returns as proof of income and financial stability. Late filers may face challenges in obtaining such services or may be subject to higher interest rates or less favourable terms.
In extreme cases or repeated late filings, there may be legal consequences such as fines, penalties, or even criminal charges depending on the jurisdiction. It is important to comply with tax regulations and fulfil obligations within the specified deadlines.
The taxpayer is subject to steep fines if the returns are not filed by the deadline. If the returns are not filed, in addition to penalties, the person may also experience various hassles and repercussions. Individuals may be subject to fines between Rs. 1,000 and Rs. 10,000 depending on how late their returns are filed.
| Date of Filing | Penalty for Income below INR 5 lakhs | Penalty for Income AboveINR 5 lakhs |
| Before July 31st | NIL | NIL |
| 1st September to 31st December | INR 1,000 | INR 5,000 |
| 1st January to 31st March | INR 1,000 | INR 10,000 |
Filing ITR plays a significant role in obtaining business loans in India. Lenders, such as banks and financial institutions, often require tax returns as crucial documents during the loan application process. Here’s how ITR is connected to business loans:
ITR serves as concrete proof of an individual or entity’s income. Lenders assess the financial stability and repayment capacity of a borrower before approving a business loan. By analyzing the income details provided in the ITR, lenders can evaluate the applicant’s ability to repay the loan.
Lenders rely on the information provided in a borrower’s tax return, known as the ITR, to evaluate their creditworthiness. The ITR reflects the financial status and operations of the entity, offering insights into revenue, expenses, and profit. By assessing the borrower’s ITR, lenders can gauge their ability to repay a loan and make informed decisions about loan eligibility, loan amount, and interest rates. Higher income levels and consistent tax filings can increase the likelihood of obtaining a larger loan with more favourable terms.
Lenders verify the authenticity of the income declared by cross-checking it with the ITR filed. Inaccurate or false information in the tax returns can raise concerns about the borrower’s credibility and may lead to business loan rejection.
Business loans are often sought to fund expansion plans, purchase assets, or invest in new ventures. Lenders evaluate the viability of the proposed business plans and the potential return on investment. The ITR, showcasing the business’s financial performance and profitability, becomes a crucial document in determining whether the business loan should be sanctioned for the intended purpose.
ITR substantiates the income, verifies the financial stability, and establishes the creditworthiness of the borrower. Timely and accurate filing of ITRs can enhance the chances of securing business loans with favourable terms and enable entrepreneurs to fuel business growth and fulfil their aspirations.

According to a recent poll by Kinara Capital, a top Fintech, small businesses often have trouble filing their GST and income tax returns on time. MSMEs need expert advice when it comes to accounting, GST registration, and tax preparation for their businesses. As per the findings of the research, a significant proportion (30%) of MSMEs highlight their requirement for non-financial services, with the primary focus being on business accounting and GST filing. GST filing constitutes a share of 17%, whereas tax calculations account for 13%.
Government and financial inclusion play a crucial role in supporting MSMEs by simplifying processes and providing guidance. By offering expert advice and assistance with accounting, GST registration, and tax preparation, they can address the challenges faced by small businesses, as identified in the poll by Kinara Capital, ensuring timely filing of GST and income tax returns and promoting the growth of MSMEs.
Income tax and income tax returns play a pivotal role in India’s economic framework. Understanding the nuances of income tax laws, tax slabs, deductions, and exemptions empowers individuals and small businesses to manage their tax liabilities more effectively. By adhering to the provisions and filing income tax returns promptly, taxpayers contribute to the nation’s revenue and ensure compliance with the legal framework governing taxation in India.
Filing ITR serves as a transparent record of an individual or entity’s income, facilitates financial planning, and helps in accessing various financial services. Timely filing of ITR ensures compliance with tax laws and contributes to the nation’s revenue collection.
However, it is crucial to understand the implications of late filing. Late filing can attract penalties and interest charges, which can result in financial consequences for taxpayers. It is advisable to file the ITR within the specified due dates to avoid unnecessary penalties and complications.
To ensure a smooth and hassle-free ITR filing process, taxpayers can leverage the convenience of e-filing through the income tax department’s official website or authorized intermediaries. Seeking assistance from tax professionals or using tax filing software can also help in accurate and timely filing.
Ultimately, maintaining a proactive approach towards tax compliance and staying updated with the latest regulations and deadlines is essential. By fulfilling our tax responsibilities promptly, we contribute to the nation’s development and promote a transparent and accountable financial system.
